python多线程教程_python零基础怎么学
Hi,大家好,我是编程小6,很荣幸遇见你,我把这些年在开发过程中遇到的问题或想法写出来,今天说一说
python多线程教程_python零基础怎么学,希望能够帮助你!!!。
目录
前言
一、进程
1.多任务
2.进程
3.多进程完成多任务
3.1进程的创建步骤
3.2通过进程类创建进程对象
3.3创建进程和启动的代码
4. 进程执行带有参数的任务
5.获取进程编号
6.进程的注意点
6.1主进程会等待所有的子进程执行结束后再结束
6.2设置守护主进程(主完子销)
二、多进程实现视频文件夹高并发copy器
三、线程
1.多任务
2.多线程完成多任务
2.1线程的创建步骤
2.2通过线程类创建线程对象
2.3线程创建与启动代码
3.线程执行有参数的任务(和进程基本一样)
4.主线程和子线程的结束顺序
4.1主线程会等待所有的子线程执行结束后再结束(同进程一样)
4.2设置守护子线程(主完子销)(同进程一样)
5.线程间的执行顺序
5.1获取当前的线程信息
四、多线程实现视频文件夹高并发copy器
五、进程和线程对比
总结(其他博客总结)
前言
这篇博客的笔记摘录自B站黑马程序员的《python多线程编程》的视频,原视频的地址如下:(博客中的代码全是我手敲的,运行皆可通过,若有错误,欢迎评论指出)
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1fz4y1D7tU?spm_id_from=pageDriver
在学习多线程编程之前,需要学会:基础语法、文件操作、模块应用
开发工具:PyCharm
内容安排:进程、线程、多任务应用
一、进程
1.多任务
同一时间内执行多个任务
主要有两种方式:
① 并发(在一段时间内交替去执行多个任务:任务数量大于CPU核心数<切换速度很快>)
② 并行(在一段时间内真正同时一起执行多个任务:任务数量小于或等于CPU核心数)
2.进程
进程(Process)是资源分配的最小单位,它是操作系统进行资源分配和调度运行的基本单位,通俗理解,一个正在运行的程序就是一个进程,例如正在运行的……
程序是静态,进程是动态
3.多进程完成多任务
3.1进程的创建步骤
①导入进程包 import multiprocessing ②通过进程类创建进程对象 进程对象 = multiprocessing.Process() ③启动进程执行任务 进程对象.start()3.2通过进程类创建进程对象
3.3创建进程和启动的代码
实例:
''' 时间:2021.8.11 作者:手可摘星辰不去高声语 名称:02-使用多进程实现多任务.py ''' # 1.导入包和模块 import multiprocessing import time def sing(): for i in range(3): print("i am sing ooo~") time.sleep(0.5) def dance(): for i in range(3): print("i am dance lll~") time.sleep(0.5) if __name__ == '__main__': # 2.使用进程类创建进程对象 # target :指定进程执行的函数名,不加括号 sing_process = multiprocessing.Process(target=sing) dance_process = multiprocessing.Process(target=dance) # 3. 使用进程对象启动进程执行指定任务 sing_process.start() dance_process.start()结果:
4. 进程执行带有参数的任务
''' 时间:2021.8.11 作者:手可摘星辰不去高声语 名称:03-进程中执行带有参数的任务.py ''' # 1.导入包和模块 import multiprocessing import time def sing(num, name): for i in range(num): print(name) print("---i am sing ooo~") time.sleep(0.5) def dance(num, name): for i in range(num): print(name) print("i am dance lll~") time.sleep(0.5) if __name__ == '__main__': # 2.使用进程类创建进程对象 # target:指定进程执行的函数名,不加括号 # args:使用元组方式给指定任务传参,顺序一致(参数顺序) # kwargs:使用字典的方式给指定任务传参,名称一致(参数名称) sing_process = multiprocessing.Process(target=sing, args=(3, "猪猪")) dance_process = multiprocessing.Process(target=dance, kwargs={"name": "珊珊", "num": 2}) # 3. 使用进程对象启动进程执行指定任务 sing_process.start() dance_process.start()
5.获取进程编号
当进程中的进程数量越来越多时,如果没有办法区分主进程和子进程,那么就无法进行有效的进程管理,为了方便管理实际上每个进程都是自己编写的
获取进程编号的两种方式:
① 获取当前进程编号
os.getpid()
② 获取当前父进程编号
os.getppid()
6.进程的注意点
6.1主进程会等待所有的子进程执行结束后再结束
''' 时间:2021.8.11 作者:手可摘星辰不去高声语 名称:06-进程注意点.py ''' # 1.导入包和模块 import multiprocessing import time def work(): # 子进程工作2秒 for i in range(10): print("工作中…") time.sleep(0.2) if __name__ == '__main__': work_process = multiprocessing.Process(target=work) work_process.start() # 主进程睡眠1秒 time.sleep(1) print("主进程执行完……")
6.2设置守护主进程(主完子销)
''' 时间:2021.8.11 作者:手可摘星辰不去高声语 名称:07-进程注意点-设置守护主进程.py ''' # 1.导入包和模块 import multiprocessing import time def work(): # 子进程工作2秒 for i in range(10): print("工作中…") time.sleep(0.2) if __name__ == '__main__': work_process = multiprocessing.Process(target=work) # 设置守护主进程,主进程退出后子进程直接销毁,不再执行子进程的代码 work_process.daemon = True work_process.start() # 主进程睡眠1秒 time.sleep(1) print("主进程执行完……")
二、多进程实现视频文件夹高并发copy器
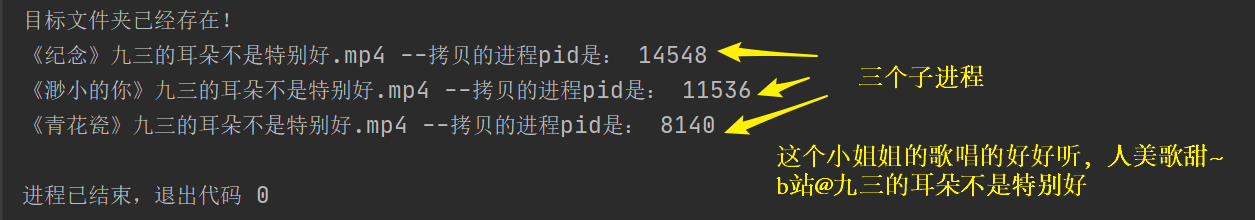
''' 时间:2021.8.11 作者:手可摘星辰不去高声语 名称:08-案例-视频文件视频的拷贝.py ''' # 1.导入包和模块 import multiprocessing import os def copy_file(file_name, source_dir, dest_dir): print(file_name, "--拷贝的进程pid是:", os.getpid()) # 1.拼接源文件路径和目标文件所在的路径 source_path = source_dir + "/" + file_name dest_path = dest_dir + "/" + file_name # 2.打开源文件和目标文件 with open(source_path, "rb") as source_file: with open(dest_path, "wb") as dest_file: # 3.循环读取源文件到目标路径 while True: data = source_file.read(1024) if data: dest_file.write(data) else: break if __name__ == '__main__': # 1.定义源文件夹和目标文件夹 source_dir = "源文件夹" dest_dir = "目标文件夹" # 2.创建目标文件夹 try: os.mkdir(dest_dir) except: print("目标文件夹已经存在!") # 3.读取源文件夹的文件列表 file_list = os.listdir(source_dir) # 4.遍历文件列表实现拷贝 for file_name in file_list: # copy_file(file_name, source_dir, dest_dir) # 5.使用多进程实现多任务拷贝 sub_process = multiprocessing.Process(target=copy_file, args=(file_name, source_dir, dest_dir)) sub_process.start()
三、线程
1.多任务
可以通过多线程的方式进行
进程是分配资源的最小单位,一旦创建一个进程就会分配一定的资源(打开两个)
线程是程序执行的最小单元,实际上进程只负责分配资源,而利用这些资源执行程序的是线程,也就是说进程是线程的容器,一个进程中最少有一个线程来负责执行程序
线程自己不拥有系统资源,但可与同属一个进程的其他线程共享进程所拥有的全部资源(一个打开两个chat窗口)
--- > 进程:
--- > 线程:
2.多线程完成多任务
2.1线程的创建步骤
①导入线程模块 import threading ②通过线程类创建进程对象 线程对象 = threading.Thread(target = 任务名) ③启动线程执行任务 线程对象.start()2.2通过线程类创建线程对象
2.3线程创建与启动代码
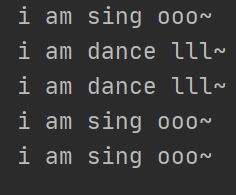
''' 时间:2021.8.11 作者:手可摘星辰不去高声语 名称:09-使用多线程实现多任务.py ''' import threading import time def sing(): for i in range(3): print("i am sing ooo~") time.sleep(0.5) def dance(): for i in range(3): print("i am dance lll~") time.sleep(0.5) if __name__ == '__main__': sing_thread = threading.Thread(target=sing) dance_thread = threading.Thread(target=dance) sing_thread.start() dance_thread.start()
3.线程执行有参数的任务(和进程基本一样)
''' 时间:2021.8.11 作者:手可摘星辰不去高声语 名称:10-使用多线程实现带参数的任务.py ''' import threading import time def sing(num): for i in range(num): print("i am sing ooo~") time.sleep(0.5) def dance(num): for i in range(num): print("i am dance lll~") time.sleep(0.5) if __name__ == '__main__': sing_thread = threading.Thread(target=sing, args=(3,)) dance_thread = threading.Thread(target=dance, kwargs={"num": 2}) sing_thread.start() dance_thread.start()
4.主线程和子线程的结束顺序
4.1主线程会等待所有的子线程执行结束后再结束(同进程一样)
4.2设置守护子线程(主完子销)(同进程一样)
设置守护子线程有两种方式:
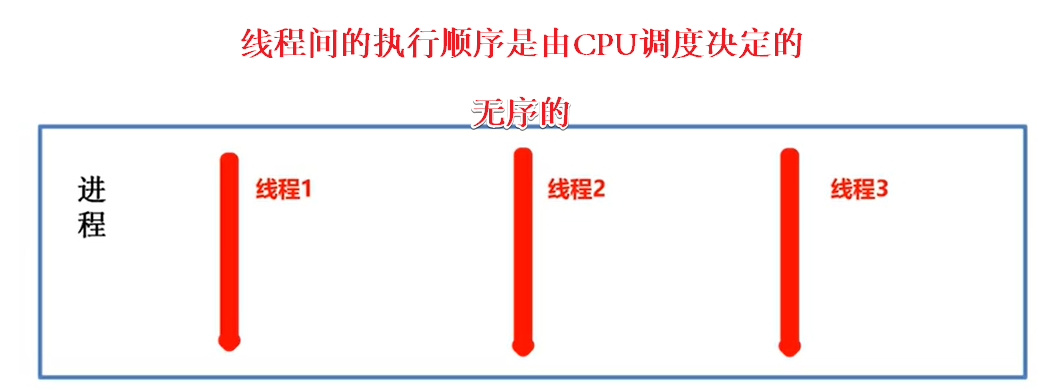
5.线程间的执行顺序
5.1获取当前的线程信息
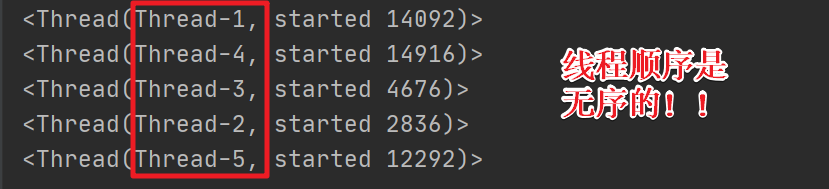
''' 时间:2021.8.11 作者:手可摘星辰不去高声语 名称:10-线程之间执行的顺序.py ''' import threading import time def task(): time.sleep(0.5) # current_thread:获取当前线程的线程对象 thread = threading.current_thread() print(thread) if __name__ == '__main__': for i in range(5): sub_thread = threading.Thread(target=task) sub_thread.start() 四、多线程实现视频文件夹高并发copy器
同进程不一样之处:
''' 时间:2021.8.11 作者:手可摘星辰不去高声语 名称:13-案例-视频文件视频多线程拷贝.py ''' # 1.导入包和模块 import threading import os def copy_file(file_name, source_dir, dest_dir): print(file_name, "--拷贝的进程pid是:", os.getpid()) print(file_name, "--拷贝的线程是:", threading.current_thread()) # 1.拼接源文件路径和目标文件所在的路径 source_path = source_dir + "/" + file_name dest_path = dest_dir + "/" + file_name # 2.打开源文件和目标文件 with open(source_path, "rb") as source_file: with open(dest_path, "wb") as dest_file: # 3.循环读取源文件到目标路径 while True: data = source_file.read(1024) if data: dest_file.write(data) else: break if __name__ == '__main__': # 1.定义源文件夹和目标文件夹 source_dir = "源文件夹" dest_dir = "目标文件夹" # 2.创建目标文件夹 try: os.mkdir(dest_dir) except: print("目标文件夹已经存在!") # 3.读取源文件夹的文件列表 file_list = os.listdir(source_dir) # 4.遍历文件列表实现拷贝 for file_name in file_list: # copy_file(file_name, source_dir, dest_dir) # 5.使用多线程实现多任务拷贝 sub_thread = threading.Thread(target=copy_file, args=(file_name, source_dir, dest_dir)) sub_thread.start()五、进程和线程对比
| 关系对比 | 线程是依附在进程里面的,没有进程就没有线程 |
| 一个进程默认提供一个线程,进程可以创建多个线程 | |
| 区别对比 | 创建进程的资源开销比创建线程的资源开销要大,进程可以用多核,但是线程不能用多核 |
| 进程是操作系统资源分配的基本单位,线程是CPU调度的基本单位 |
总结(其他博客总结)
非常详细的一篇博客:Python中线程与进程
……略
今天的分享到此就结束了,感谢您的阅读,如果确实帮到您,您可以动动手指转发给其他人。