ES6数组新方法
Hi,大家好,我是编程小6,很荣幸遇见你,我把这些年在开发过程中遇到的问题或想法写出来,今天说一说ES6数组新方法,希望能够帮助你!!!。
ES6数组新方法
目录
-
- ES6数组新方法
-
- 1. `forEach()`和`map()`
- 2. `filter()`
- 3. `reduce()`
- 4. `some()`
- 5. `every()`
- 6. `Array.from()`
- 7. `Array.of()`
- 8. `copyWithin()`
- 9. ` find() `和 `findIndex()`
- 10. `fill()`
- 11. `entries()`,`keys() `和 `values()`
- 12. `includes()`
- 13. `flat()`,`flatMap()`
- 14. `at()`
1. forEach()和map()
forEach()会修改原来的数组,不会返回执行结果。map()方法会得到一个新的数组并返回。
map的执行速度会更快。
let arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
arr.forEach((num, index) => {
arr[index] = num * 2
});
let doubled = arr.map(num => {
return num * 2;
});
// [2, 4, 6, 8, 10]
2. filter()
创建一个新数组, 返回符合条件的元素。
var arr = ['spray', 'limit', 'elite', 'exuberant', 'destruction', 'present'];
const newArr = arr.filter((arrItem,index,arr) => {
console.log(arrItem,index,arr)
return arrItem.length > 6
});
console.log(newArr);
3. reduce()
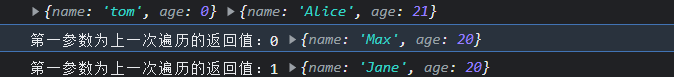
官方:对数组中的每个元素执行一个由您提供的reducer函数(升序执行),将其结果汇总为单个返回值。
简单来讲,他的主要作用,就是可以取到上次遍历的返回值。进而做累加等操作
var people = [
{
name: 'Alice', age: 21 },
{
name: 'Max', age: 20 },
{
name: 'Jane', age: 20 }
]
people.reduce(
(acc, obj, index, array )=>{
console.log(acc, obj)
return '第一参数为上一次遍历的返回值:' + index
},
{
name: 'tom', age: 0}
)
4. some()
判断数组中是不是,至少有1个元素,通过了被提供的函数。
var fruits = ['apple', 'banana', 'mango', 'guava'];
function checkAvailability(arr, val) {
return arr.some(
(arrVal) => {
return val === arrVal
}
);
}
checkAvailability(fruits, 'kela'); // false
checkAvailability(fruits, 'banana'); // true
5. every()
指数组内的所有元素是否都能通过某个指定函数
[12, 5, 8, 130, 44].every(x => x >= 10); // false
[12, 54, 18, 130, 44].every(x => x >= 10); // true
6. Array.from()
用于将类似数组的对象和可遍历对象转为真正的数组
//还可以接受第二个参数,作用类似于数组的map方法,用来对每个元素进行处理,将处理后的值放入返回的数组
Array.from([1, 2, 3], (x) => x * x)
// [1, 4, 9]
// 如果map函数里面用到了this关键字,还可以传入Array.from的第三个参数,用来绑定this
7. Array.of()
用于将一组值,转换为数组。
用来弥补数组构造函数Array()的不足,基本上可以用来替代Array()或new Array()
Array.of(3, 11, 8) // [3,11,8]
Array.of(3) // [3]
Array.of(3).length // 1
Array() // []
Array(3) // [, , ,]
Array(3, 11, 8) // [3, 11, 8]
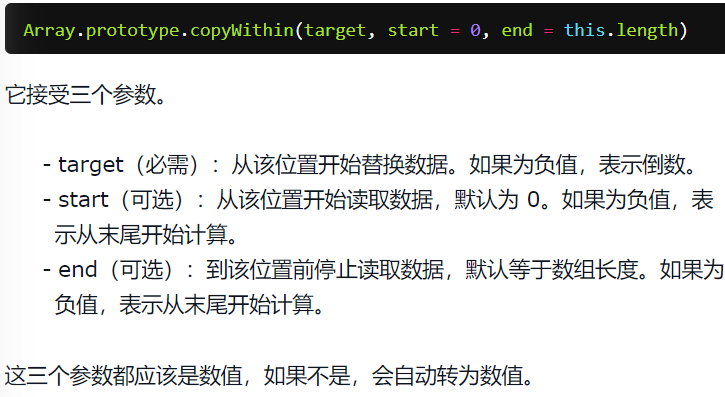
8. copyWithin()
将指定位置的成员复制到其他位置,然后返回当前数组,会修改当前数组。
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5].copyWithin(0, 3)
// [4, 5, 3, 4, 5]
9. find()和 findIndex()
// find:找出第一个符合条件的数组成员
// 回调函数可以接受三个参数,依次为当前的值、当前的位置和原数组
[1, 5, 10, 15].find(function(value, index, arr) {
return value > 9;
}) // 10
// findIndex:返回第一个符合条件的数组成员的位置,如果所有成员都不符合条件,则返回-1
[1, 5, 10, 15].findIndex(function(value, index, arr) {
return value > 9;
}) // 2
这两个方法都可以接受第二个参数,用来绑定回调函数的this对象。
function f(v){
return v > this.age;
}
let person = {
name: 'John', age: 20};
[10, 12, 26, 15].find(f, person); // 26
10. fill()
使用给定值,填充一个数组。用于空数组的初始化非常方便。
['a', 'b', 'c'].fill(7)
new Array(3).fill(7)
// [7, 7, 7]
// fill方法还可以接受第二个和第三个参数,用于指定填充的起始位置和结束位置。
['a', 'b', 'c'].fill(7, 1, 2)
// ['a', 7, 'c']
// 如果填充的类型为对象,那么被赋值的是同一个内存地址的对象,而不是深拷贝对象
11. entries(),keys() 和 values()
用于遍历数组。它们都返回一个遍历器对象。
keys()是对键名的遍历、values()是对键值的遍历,entries()是对键值对的遍历
for (let index of ['a', 'b'].keys()) {
console.log(index);
}
// 0
// 1
for (let elem of ['a', 'b'].values()) {
console.log(elem);
}
// 'a'
// 'b'
for (let [index, elem] of ['a', 'b'].entries()) {
console.log(index, elem);
}
// 0 "a"
// 1 "b"
12. includes()
表示某个数组是否包含给定的值,方法返回一个布尔值。
[1, 2, 3].includes(2) // true
[1, 2, 3].includes(4) // false
[1, 2, NaN].includes(NaN) // true
// 第二个参数表示搜索的起始位置,默认为0, 支持负数
[1, 2, 3].includes(3, 3); // false
13. flat(),flatMap()
flat:用于将嵌套的数组“拉平”,变成一维的数组。返回一个新数组
flatMap:对原数组的每个成员执行一个函数,然后对返回值组成的数组执行flat()方法,返回一个新数组。
[1, 2, [3, [4, 5]]].flat()
// [1, 2, 3, [4, 5]]
[1, 2, [3, [4, 5]]].flat(2)
// [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
[1, [2, [3]]].flat(Infinity)
// [1, 2, 3]
// 会跳过空位
[1, 2, , 4, 5].flat()
// [1, 2, 4, 5]
// flatMap()只能展开一层数组
[2, 3, 4].flatMap((x) => [x * 1, x * 2])
// [2, 4, 3, 6, 4, 8]
// 相当于 [[2, 4], [3, 6], [4, 8]].flat()
// flatMap()方法的参数是一个遍历函数,该函数可以接受三个参数,分别是当前数组成员、当前数组成员的位置(从零开始)、原数组。
// flatMap()方法还可以有第二个参数,用来绑定遍历函数里面的this。
arr.flatMap(function callback(currentValue[, index[, array]]) {
// ...
}[, thisArg])
14. at()
接受一个整数作为参数,返回对应位置的成员,主要是为了解决运算符[]不支持负索引。
const arr = [5, 12, 8, 130, 44];
arr.at(2) // 8
arr.at(-2) // 130
接着看es5的数组方法:
点这里:js数组方法
今天的分享到此就结束了,感谢您的阅读,如果确实帮到您,您可以动动手指转发给其他人。
上一篇
已是最后文章
下一篇
已是最新文章